LEARN MORE
Letrozole (Femara) for Fertility
Letrozole can stimulate ovulation in people with PCOS
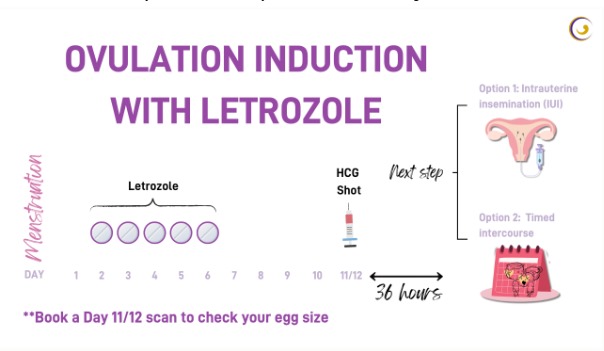
Letrozole, an oral medication, is used to induce ovulation in individuals with PCOS and unexplained infertility. Letrozole has been widely adopted off-label for fertility treatment due to its favourable side effect profile compared to the previous indication, Clomid and lower incidence of multiple pregnancies.
Research suggests that Letrozole may offer higher pregnancy rates in PCOS patients, potentially surpassing Clomid in efficacy. In some cases, a combination of Clomid and Letrozole is also effective for inducing ovulation. Letrozole is recommended as a first-line treatment for PCOS patients with ovulation issues, especially in cases of Clomid resistance. It is typically taken orally over five consecutive days, with variations in the recommended treatment days.
Letrozole can also be used for intrauterine insemination (IUI) treatment. Side effects may include bloating, blurred vision, breast pain, and fatigue, with rare instances of ovarian hyperstimulation syndrome (OHSS). Studies demonstrate higher ovulation and birth rates with Letrozole compared to Clomid, along with a lower incidence of multiple pregnancies. Letrozole is considered effective and safe for various fertility treatments, including unexplained infertility, ovarian stimulation, endometriosis-associated infertility, and fertility preservation during cancer treatment. Overall, Letrozole appears promising and cost-effective for fertility treatment across different scenarios.
FSH Injection
- FSH stands for follicle stimulating hormone and is a hormone produced by the brain to stimulate egg production in the ovaries. It is released in variable amounts through a natural cycle to result in one egg being available for fertilisation.
- Sometimes if you are not ovulating, FSH is given in an amount roughly equal to that of a natural cycle and this is called ovulation induction. The goal is to produce one or occasionally two ripe eggs only.
- At other times the intention may be to produce 2 to 3 eggs and this is called superovulation. This is often used to treat unexplained infertility and infertility after treatment of endometriosis. This may be combined with placement of your partner’s sperm in your uterus (insemination).
- While you are taking FSH injections you will need to visit your doctor once or twice for a scan and possible blood test to see how many and how well the eggs are doing.
- Once the scan shows that there are enough follicles and they are big enough, a ‘trigger’ injection is given to stimulate ovulation.
- You may then be advised to have intercourse or insemination
LAPAROSCOPIC SURGERY
Laparoscopic Surgery is a modern surgical technique used to examine the abdominal or pelvic regions using a slender tube (laparoscope) inserted through a small incision in the abdomen. This operation uses tiny surgical instruments and a small camera to view the desired area.
Instead of making a large incision or cutting for the operation, incisions are usually between 0.5 and 2.5cm. For this reason, it is also sometimes called:
- Minimally invasive surgery
- Keyhole surgery
One of the potential significant advantages of Laparoscopic Surgery is that recovery time may be significantly less than traditional surgery.
Source – Better Health Channel
- How can Laparoscopic Surgery help?
Laparoscopic Surgery may help Dr. Myran diagnose and treat endometriosis, infertility, and other problems such as fibroids. It can also help view the urinary system and remove cancer and excess fluid in the pelvic cavity.
Note – Dr. Myran Operates privately through Waverley Private Hospital.
- How long does it take?
The surgery usually takes up to an hour.
Patients must be checked in at the hospital 45 minutes before the operation. Once ready, you may wait in the operating theatre for about 10-15 minutes before the operation starts.
- Anaesthetic
Laparoscopy is performed under a general anaesthetic.
- The incision and operation
A small incision (usually next to the navel),, and the laparoscope is inserted into the abdominal cavity. Carbon dioxide or nitrous oxide gas is then passed into the cavity to separate the abdominal wall from the underlying organs. This allows Dr. Myran to examine the internal organs.
Additional incisions (up to three) allow access to other necessary surgical instruments. Once a diagnosis is made or the problem is removed (or both), the instruments are removed, the gas is allowed to escape, and the incisions are sewn shut. The stitches may need to be removed by the doctor later, or they will dissolve by themselves.
- Postoperative recovery
Most patients usually spend 30 to 60 minutes in recovery after surgery. You should be up and walking around soon after.
After the procedure, you may experience:
- Soreness around the incision site/s
- Shoulder pain caused by the gas pumped into the abdominal cavity
- A sensation of abdominal bloating
- Nausea
- Abdominal cramps
- Constipation
- For pelvic procedures only, light bleeding or discharge from the vagina
Remember to plan and discuss pain-relieving treatments post-operation.
Important notes
- Please do not drive home following laparoscopy.
- The medication used during the procedure can temporarily inhibit physical and mental abilities. Have a friend or relative take you home from the hospital or call a taxi.
- Most symptoms of laparoscopic surgery resolve within one or two days.
- If you experience severe abdominal pain, fainting, fever, or vaginal bleeding, please contact our rooms or your nearest emergency department.
**Please note that our procedures are performed at the East Melbourne Specialist Hospital.**
Ultrasound
- What is an Ultrasound examination?
Ultrasound is an image technique which use high frequency sound waves to obtain pictures of the inside of the body without the use of X-rays. It is safe and generally a painless procedure.
- What is the purpose of the Transvaginal ultrasound?
The transvaginal (internal) ultrasound scan does not require a full bladder. This type of scan is used to help provide clearer images of the womb, ovaries and surrounding structures. This form of scan helps with better understanding of the female reproductive system.
- What preparation is needed for the test?
You do not need a full bladder for this scan so you will need to empty your bladder completely prior to the scan. If you are using a tampon, this will need to be removed before the scan. You will not be asked to have a vaginal ultrasound is you are unable to tolerate vaginal (internal) examinations or if you are not sexually active or are a virgin. You should continue to take any medications prescribed by your doctor. Please note that an internal scan can be performed at any time during a women’s life – in pregnancy, during period or after menopause. If you have any concerns about this procedure, please discuss with Dr Ponnam-Palam who will be performing the examination.
- How is it performed?
For a transvaginal (internal) ultrasound scan, once you have emptied your bladder, we will ask you to undress completely from the waist, down and cover your waist with the sheet provided. If you are wearing a skirt/dress, you may prefer to just remove your underwear. You will be asked to lie on your back on the ultrasound couch and position yourself in a way that allows the scan to be performed easily. This will involve raising your knees and placing your legs in the stirrups. A specially designed ultrasound probe is used for this procedure. It will be covered with a protective sheath and lubricant gel, then gently inserted into your vagina. The ultrasound probe will need to be moved in different positions to visualise the uterus and ovaries clearly.
Tubal Patency Test/Saline Scan
- What is the purpose of the Tubal Patency procedure?
This procedure is usually recommended to some women who might be having difficulty conceiving, as it detects any blockages in the fallopian tubes. The fallopian tubes are a pair of thin tubes connecting the ovaries to the uterus. In reproduction, an ovary bursts, releasing an egg, which then travels along the fallopian tube and into the uterus.
Therefore, to obtain a pregnancy the tubes must be open and clear from any blockages. When there are tubal blockages, this prevents the egg from meeting the sperm, so it becomes very difficult or impossible for conception to take place.
In some women, there appears to be a slightly better pregnancy chance after the tubal patency test. This may be due to possibly clearing of any mucus plug blockage.
A new non-blocked fallopian tube allows you to proceed through simple fertility treatment options. While, if tubes are blocked, then IVF is generally the recommended treatment.
If your doctor wants to test whether or not your fallopian tubes are clear, they will often refer you for a Tubal Patency Procedure. It is wise to check with your referring doctor before this procedure to ensure you will not be allergic to the ‘solution’ which will be used during the procedure.
- What preparation is needed for the test?
We actually require you to have an empty bladder, so we’ll just get you to go to the bathroom when you arrive for your appointment. As some patients might have a slight pain during the procedure, we usually advise them to take painkillers before coming to the procedure.
- How is it performed?
Before the procedure commences, the doctor will explain the procedure to you step-by-step and ensure you are informed at every stage of the procedure. Our doctor is a fully qualified Gynaecologist, Obstetrician and Sonologist who has extensive experience in this procedure.
A trans-vaginal ultrasound is performed first to assess the pelvic anatomy. A speculum is then inserted into the vagina and an antiseptic solution is used to clean the vagina and the cervix. A very thin plastic tube called a catheter with a small size balloon at the tip, is inserted into the cervix. Once the tip of the catheter is in the uterine cavity, the balloon is inflated using a tiny amount of sterile saline (salt solution). This helps keep the catheter in place. The enlargement of the uterine cavity associated with the inflation of the balloon may cause some pain due to cramping of the uterus, however patients have stated that it is no more uncomfortable than a pap smear.
The speculum is then removed and a thin ultrasound probe is inserted into the vagina. The ‘solution’ is then injected through the catheter illuminating the fallopian tubes on the ultrasound and hopefully spilling around the ovary on both sides.
Without using the ‘solution’ the fallopian tubes cannot be seen on a regular ultrasound therefore it is necessary to inject the ‘solution’ contrast.
- Are the results accurate?
If one or both tubes are not patent or open then this becomes obvious during the procedure. The fallopian tubes are diagnosed open if the spilling of the Levovist solution is seen on both sides of the ovaries.
However, if the solution does not spill over the ovaries, this does not necessarily conclude that they are blocked as the uterus can temporarily spasm and obstruct the opening of fallopian tubes. If this is the case, further assessment will be arranged.
- When should the test be performed?
The test should be performed between days 3 to 10 of your menstrual cycle – day 1 being the first day of bleeding. If you do not have a regular cycle then your doctor will inform you of the appropriate time to have the procedure done.
If you are currently ovulating (which is a phase of the female menstrual cycle, that involves the release of an egg (ovum) from one of the ovaries), or an abnormality is noted on the ultrasound the procedure will not be performed and will consequently be delayed to an appropriate time in your next cycle.
However, if the ultrasound findings are normal and consistent with the first half of the menstrual cycle, the procedure will be performed.
Hysteroscopy
Hysteroscopy is a minor procedure that helps Dr. Myran look inside the uterus to help assess, diagnose, or treat infertility problems for patients experiencing heavy periods, abnormal vaginal bleeding, fibroids, and polyps.
A hysteroscope is a thin, telescope-like device that is inserted into the uterus through the vagina and cervix. A sample of the lining is often taken to be sent off for further examination. This procedure does not involve any incisions to the abdomen and takes about 10-15 minutes, but recovery can be several hours. The procedure is performed under local or general anaesthesia.
- What can you expect?
Hysteroscopy is a minor procedure that may be done in Dr. Myran’s clinic or a hospital.
After the procedure, you may experience:
- Pelvic discomfort
- Nausea
- Abdominal cramps
- For pelvic procedures only, light bleeding or discharge from the vagina
Note – Most symptoms of hysteroscopy surgery resolve within one or two days – if not, see your doctor.
Important note
Patients are advised not to drive home following hysteroscopy due to the medication given before the procedure – Ensure you have a relative or friend to take you home from the hospital or call a taxi.
**Please note that our procedures are performed at the East Melbourne Specialist Hospital.**
Preparing for Day Surgery
- What time do you need to be at the hospital?
The friendly hospital staff will inform you when you must be there.
Note – Dr. Myran operates privately through Waverley Private Hospital.
- How long will you be in hospital?
The length of stay varies from person to person. Once we know that you are well enough to leave, you will be discharged. It is usually a day procedure, so you go home the same day.
- What do you need to do to be ready for day surgery?
- Before surgery, you must not eat or drink anything (including water and chewing gum)
- For morning surgery, do not have anything after midnight
- For afternoon surgery, do not have anything after 7.00 am on the day of surgery
- Stop smoking at least 12 hours before surgery
- If you are currently taking any medications, please inform Dr. Myran. He must know what medications you are taking before any surgery.
- If Dr. Myran has approved your medications, and you are due to take them on the day of your surgery, take them with only one mouth full of water.
- Avoid taking Aspirin for two weeks before surgery.
Important considerations
If you develop a cough or fever in the week before your surgery, please inform Dr. Myran.
If you are sexually active, you may need to have a pregnancy test depending on the last day of your period (before your procedure).
| Please bring/wear them to the hospital | Please do not bring or wear |
|---|---|
|
|
Private patients are asked to please settle their hospital account on admission. If you do not have a private health insurance card, you must pay cash, cheque, or credit card at the accounts office.
- What can you expect?
You will be walked/shown into the operating theatre. After your procedure, you will rest in the recovery area. The friendly nursing staff will look after you and offer you refreshments.
When you feel well enough, you can dress and wait until the medical team discharges you.
Your support person, friends, or relatives are welcome to wait at the hospital during your stay. Visitors may wish to spend time in our coffee shop.
- Going home
You will need to arrange for someone to take you home after surgery. You will also need to have someone with you overnight. You will need to collect from the day surgery unit.
AFTER DAY SURGERY
For 24 hours following an anaesthetic you should not:
- Drive a car
- Operate machinery or electrical appliances
- Drink alcohol
- Sign any legal documents
- Make any major decisions
Once you are home, Please follow the Postoperative instructions sheet we will give you. You may need to return for a follow-up appointment. If so, information about your appointment will be posted to you.
Clomid Usage Under the Care of Dr. Myran
- What is Clomid?
Clomid is a fertility drug used to induce ovulation and comes in tablet form. It’s generally used as a first step in fertility treatment – Source: Drugs.com
Clomid is taken for a certain number of days after your menstrual cycle.
- What happens when I am taking Clomid?
During your prescribed Clomid cycle, your ovarian response to the medication will be monitored using an ultrasound and sometimes a blood test.
This allows Dr. Myran to assess the best time for you and your partner to have unprotected intercourse or through insemination.
- How does Clomid work to induce ovulation?
Clomid works essentially by tricking your body into producing more follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH) and luteinizing hormone (LH), which in turn will hopefully cause your body to ovulate.
Clomid essentially blocks estrogen in the ovulation process. This causes your body to think there is not enough estrogen, and your body works hard to produce more. This causes a chain reaction in additional hormone production to help your body to ovulate.
- Step-by-step instructions:
Step 1 – Day 1 is the day of onset of your period.
Once your period starts, please call the office (if instructed) to make an appointment for a scan on days 11, 12, or 13 of your menstrual cycle.
Step 2 – Starting on day 3, 4, or 5 after the onset of your period, take one Clomid pill every day for 5 days.